Page Content
CONTENTS
Issuing
Internet Payment Gateway
Payment Gateway
A payment gateway is an e-commerce application service provider that authorises direct or credit card payment processing for online retailers, e-businesses, brick-and-mortar establishments, and bricks and clicks. Banks and specialised financial service providers may provide payment gateways. The technology aims to facilitate payment transactions by transferring information between payment portals (mobile phones, websites, interactive voice response services) and acquiring banks or front-end processors. Payment gateways are a service that helps companies initiate in-app, e-commerce, and point-of-sale payments. It isn’t directly involved in the money flow. It’s typically a web server to which a merchant’s POS solution or website is connected. Payment gateways often link several acquiring banks and various payment methods under a single system.Payment Gateway vs Internet Payment Gateway
Payment gateways are software applications that enable online transactions by transferring data between mobile devices, websites, and POS systems. IPGs, on the other hand, are developed to process online payments. Internet Payment Gateways offer a secure platform for processing online transactions while protecting sensitive data. They facilitate operations through payment cards and digital wallets such as PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Venmo, Samsung Wallet, etc. In addition, IPGs offer a range of features, including but not limited to real-time payment processing, transaction reporting, and fraud detection and prevention. The most common types of payment gateways are:- Hosted – They redirect customers to a separate payment page during checkout.
- Non-Hosted – Used to integrate payment processing into the merchant’s mobile application or website.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor
Many people wrongly believe that a payment gateway and a payment processor are the same technology. Some go as far as thinking they are interchangeable terms. In reality, they are very distinct from one another. Payment gateways collect customer information for payment, while payment processors use the gathered data to contact the client’s bank and the merchant account to debit one and credit the other. Essentially, they are the two halves of the transaction.Typical Transaction Processes
When a client orders a product from a payment gateway-enabled business, the payment gateway executes several tasks to process the transaction, as shown in the graphic below.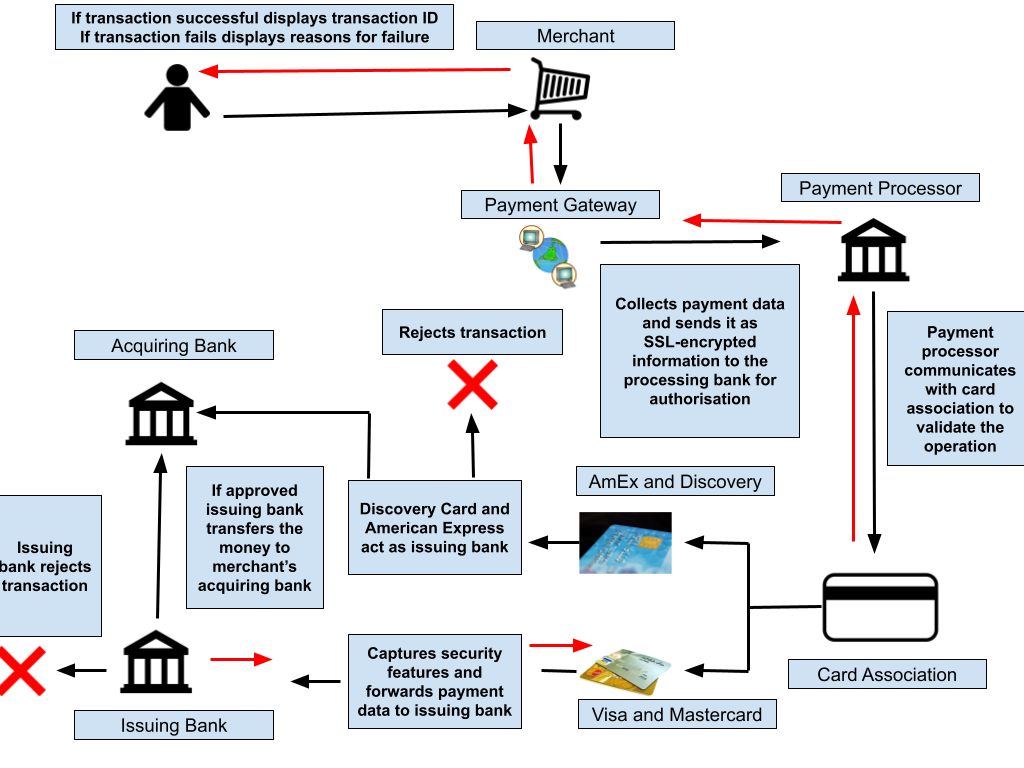 Many payment gateways also provide the technologies to automatically screen orders for fraud and calculate tax in real time before the authorisation request is sent to the processor. Tools used to detect fraud can include:
Many payment gateways also provide the technologies to automatically screen orders for fraud and calculate tax in real time before the authorisation request is sent to the processor. Tools used to detect fraud can include:
- Velocity pattern analysis;
- Delivery address verification;
- Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) list lookups;
- Computer fingerprinting technology;
- Geolocation;
- Identify morphing detection;
- ‘Deny-list’ lookups;
How Payment Gateways Benefits Businesses
Payment gateways can help businesses improve in the following three sectors:- Convenience – Companies with an integrated payment gateway enable their clients to make purchases at any time. Allowing customers to shop at leisure adds convenience, automatically enhancing the overall experience.
- Better Security – Payment gateways considerably lower the risk of credit card fraud because:
- Card information is securely transmitted, meaning only the card owner and issuing bank can access it.
- Card services offer a supplementary security protocol (3-D Secure), which requests the card owner to create a password for every card they use to make an online payment.
- All payment gateways must comply with PCI DSS standards to ensure that card data is processed securely.
- Faster Payments – Payment gateways enable clients to pay for their goods instantly, saving them time. They also help businesses collect their earnings more rapidly.