Page Content
CONTENTS
Issuing
SWITCH
SWITCH is a tool that facilitates communication between different payment networks. It offers merchant-driven, rules-based switching solutions and authorisation. It dynamically routes payment transactions between acquirers and Payment Service Providers (PSPs).
SWITCH is positioned at the centre of payment processing. It acquires, directs, switches, authenticates, and authorises payment operations across multiple channels. It adds new payment methods and providers, thus enabling the expansion of payment networks.
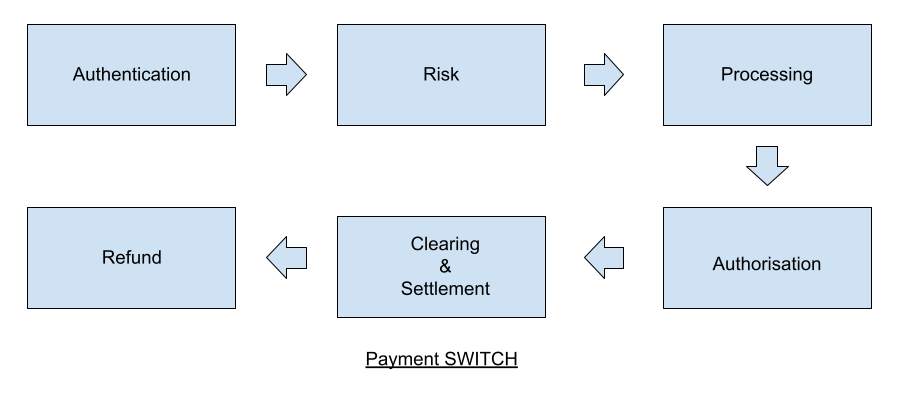
The SWITCH Process

How Does SWITCH Work?
Once a payment request is initiated, SWITCH authorises the merchant and the transaction. It uses a set of rules to determine whether an operation should be allowed. These rules include routing by:- Bank Identification Number (BIN)
- Amount
- Time of the Day
What to Look For in a Payment SWITCH?
Today, many businesses operate on a global level with multiple acquirers. To provide uninterrupted services to their clients, companies must use a payment SWITCH that complies with the following requirements:- Fraud Management – SWITCH should perfectly balance fraud management and customer experience. It should support 3D Secure (3DS) authentication and offer real-time notifications.
- Security – Security is arguably the most important factor regarding online payments. For the well-being of businesses and clients, SWITCH should comply with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), tokenisation tools, and various encryption protocols.
- Dynamic Routing – Different acquirers have different acceptance rates. SWITCH should be able to consider these variables and use them to route payment transactions dynamically. Well-designed frameworks are known to maximise payment acceptance and minimise operations failure.
- Extension of Payment Network – There are many PSPs on the market, and their number is expected to grow. Clients typically pay online with the most comfortable option. SWITCH should support the integration of numerous global acquirers and PSPs. Lowering deployment expenses for companies as they won’t require to invest in multiple technologies.
Payment SWITCH vs Payment Gateway
SWITCH and payment gateway are the two major players in the payment ecosystem. They have many similarities, but they are also different from one another. To avoid confusing them, here are some things that businesses and individuals should know.Payment Gateway
A payment gateway is a third-party software positioned between companies and issuing bank accounts. It takes care of the transaction process end-to-end, covering everything from security to settlement.Benefits of Payment Gateway
- Enables millions of users to execute payment transactions with merchants
- Allows multiple payment options (mobile wallets, net banking, card cards, or online transactions)
- Reduces fraudulent activities in online payments via different authentication steps, such as One-Time Password (OTP), Card Verification Value (CVV or CCV)
Payment SWITCH
Payment SWITCH is a technology embedded into the payment gateway. It’s an independent entity developed to assist with payment processing. Being an Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) solution, it takes care of the modulations inside a transaction.Benefits of Payment SWITCH
- Dynamic routing
- No connectivity time-out issues
- Enables payment networks extension
- Fewer outages
- Highly scalable
- Minimised fraud risk and more secure due to encrypted BIN allotment