Page Content
CONTENTS
Issuing
Digital Wallets
Digital wallets, or e-wallets, are electronic devices, software, or online services developed to help parties execute electronic transactions bartering digital currency for goods and services. It includes purchasing items online or at a point-of-sale at a brick-and-mortar store. Digital wallet owners can use mobile payment applications or internet payment gateways to transact.
Individuals can link their bank accounts to their e-wallets or deposit money before any purchase. Users can also store their driver’s licenses, loyalty cards, health cards, and other identification documents within their wallets.
The latest digital wallets are designed to do more than basic financial operations. They can also be used to authenticate the identity of their holders. For example, some e-wallets can verify the age of buyers while purchasing alcohol. Digital wallets wirelessly transmit credentials to merchant terminals through Near Field Communication (NFC) technology.
 To ensure the privacy and security of user data and transactions, developers deploy different security measures, such as encryption, Know Your Customer (KYC), and multi-factor authentication, to name a few. They can also set limits for certain operations.
To ensure the privacy and security of user data and transactions, developers deploy different security measures, such as encryption, Know Your Customer (KYC), and multi-factor authentication, to name a few. They can also set limits for certain operations.
Technology
E-wallets have an information component and software. The latter provides security and encryption for transactions and the owner’s data. The information component is a database of user-input data, including billing addresses, payment methods, shipping addresses, and more. Digital wallets are kept on the client side, are fully compatible with most e-commerce websites, and are easily self-maintained. Server-side wallets are known as thin wallets and are created by organisations for their clients. This e-wallet type is stored on servers and is gaining popularity among retailers due to its efficiency, security, and additional utilities, increasing overall customer satisfaction. Digital wallets are composed of e-wallet devices and systems. Dunhill’s biometric wallet is a physical device that holds cards and cash and uses Bluetooth to connect to smartphones, tablets, or laptops. There are further explorations for mobile phones with NFC capabilities. Apple and Google are developing their operating systems to power their wallets, Apple Pay and Google Pay. E-wallet systems permit the widespread use of digital wallet transactions among businesses through mobile payment platforms and e-wallet applications. The M-PESA mobile payments system and microfinancing service are common in Tanzania and Kenya. Alternatively, many United States and worldwide vendors have adopted the MasterCard PayPass application. One in every five countries in Asia is now using a digital wallet. It represents a twofold increase from previous years. A Mastercard mobile shopping survey shows that the Chinese, Indians, and Singaporeans are among the biggest adopters of e-wallets. Further analysis demonstrated that approximately 49% of consumers in these regions had purchased through their smartphones. Indians are leading the way, with 76.4% using a phone to pay for purchases. These results have inspired companies like Amazon India and Reliance to develop their own digital wallets.Security
When using an e-wallet, consumers aren’t required to fill out order forms as their information is stored on the device and automatically updated and entered into the order fields across merchant websites. Digital wallets also provide enhanced protection to personal data as the stored information is encrypted or safeguarded by a private software code. Merchants, in contrast, benefit by receiving a faster receipt of payment, decreased transaction costs, minimised theft loss, and a combination of protection against fraud. E-wallets are available free of charge and are relatively easy to obtain. Although free for consumers, vendors charge merchants who wish to offer server-side digital wallets. Some wallet developers make arrangements with businesses to pay them a percentage of every successful purchase executed via their products. In other cases, vendors process transactions between cardholders and merchants and charge the latter a flat fee.Cryptocurrency Wallets
Digital currency isn’t the only currency that can be stored on e-wallets. Consumers can also use their wallets to store cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Binance Coin, Tether, XRP, etc. Cryptocurrency wallets are divided into two categories: hot wallets and cold wallets.Hot Wallets
Hot crypto wallets are connected to the Internet and are widely adopted because of their capability to transfer and receive funds on demand. They offer different features, from sending, receiving, and storing tokens to managing and viewing all available tokens in a single place. They are accessible from Internet-enabled devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. Two key components keep digital assets safe in a cryptocurrency wallet: the private and public keys. A cryptographic string of letters and numbers responsible for successful crypto transfers makes both. Private keys are designed to verify token ownership. With them, crypto owners can exchange their currency. Public keys enable cryptocurrency transactions. They are similar to an account username. Types of Hot Wallets There are different types of hot wallets with various purposes. Some are used as mobile applications, others are web-only, and others are ecosystem-specific. The list is sizeable, and wallet usage depends mainly on its owner’s needs. Some of the most popular hot wallets are:- Coinbase Wallet;
- Trust Wallet;
- MetaMask;
- Robinhood;
- Edge;
- Exodus Wallet;
- Design;
- Fees;
- Integration;
- Crypto exchange compatibility;
Cold Wallets
Unlike hot wallets, cold wallets aren’t Internet-enabled. Thus, they’re less prone to cyber-attacks. This fact is the primary reason they have gained rapid popularity and adoption, especially after the collapse and bankruptcy of FTX in November 2022, which left many wallet owners’ digital assets frozen or gone. Cold wallets come as hardware devices, typically a USB stick. An added security layer comes from private keys being entirely offline and required to execute a crypto exchange. Types of Cold Wallets Some of the most common types of cold wallets are:- Deep Cold Storage – This type of cold wallet takes extra steps to make access difficult. They are developed for users who require minimal access to their digital assets. An analogy would be keeping a cold wallet in a physical deposit box or vault.
- Paper Wallet – A printed document containing the wallet’s public and private keys. The paper also features an embedded Quick Response (QR) code to ease crypto transactions. It is the least secure and most susceptible to damage of all types of cold wallets.
- Hardware Wallet – A ubiquitous cold wallet consisting of offline devices that store private and public keys. Usually, they come in the form of smart cards or thumb drives, without which users cannot access their cryptocurrency. Popular hardware wallets are Ledger, KeepKey, and Trezor.
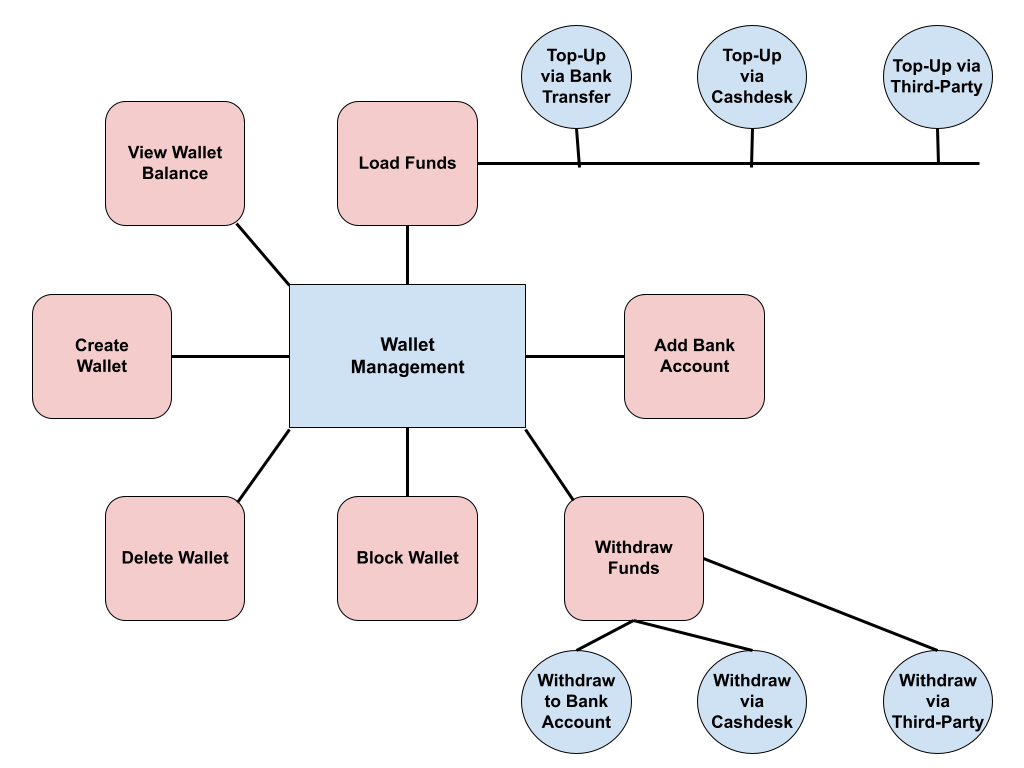
Wallet Management
Vendors and companies use wallet management platforms to manage user wallets, funds, and transactions within a system. The wallet management process involves the following steps:- Wallet creation;
- Checking wallet balance;
- Top-up wallets;
- Funds withdrawal;
- Adding bank account;
 To ensure the privacy and security of user data and transactions, developers deploy different security measures, such as encryption, Know Your Customer (KYC), and multi-factor authentication, to name a few. They can also set limits for certain operations.
To ensure the privacy and security of user data and transactions, developers deploy different security measures, such as encryption, Know Your Customer (KYC), and multi-factor authentication, to name a few. They can also set limits for certain operations.